커밋
633295b0f8
7개의 변경된 파일과 163개의 추가작업 그리고 0개의 파일을 삭제
+ 104
- 0
README.md
파일 보기
| # NGS Check mates | |||||
| > Author: Ren Luyao | |||||
| > | |||||
| > E-mail: 18110700050@fudan.edu.cn | |||||
| > | |||||
| > Git: http://choppy.3steps.cn/renluyao/NGScheckMates.git | |||||
| > | |||||
| > Last Updates: 2019/02/08 | |||||
| ```bash | |||||
| source activate choppy | |||||
| choppy install renluyao/NGScheckMates | |||||
| ``` | |||||
| # APP概述 | |||||
| NGScheckMates是用来检测某几个测序数据是否来自于同一个人,有以下几种应用场景: | |||||
| (1)多组学研究,RNAseq和DNAseq是否是来自同一个人; | |||||
| (2)被标注为配对的Tumor和Normal样本是否是来自同一个人; | |||||
| (3)同一批样本,多次测序,其中有没有被标错的样本。 | |||||
| 推荐直接用fastq模式,优点:如果有多种不同测序文件,比如一个项目中有WES和RNAseq,你要研究WES找到的候选突变是否影响了基因表达量的改变,你需要检查WES和RNAseq的数据是否来自同一个人,以确保分析结果的正确性。直接用fastq模式可以不用单独对RNAseq call germline mutation,以节省时间。这一步将单独运行一个脚本。 | |||||
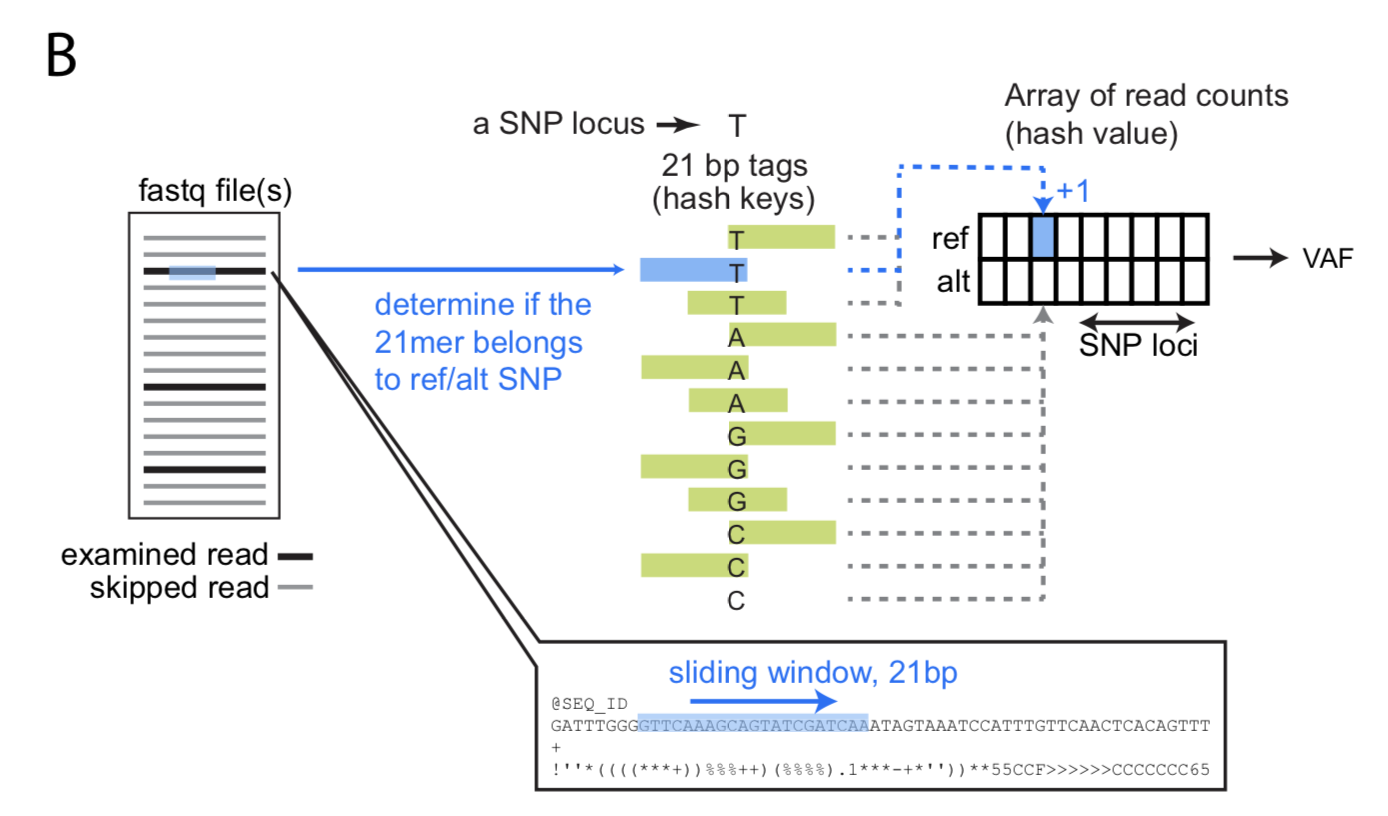
| 基于fastq文件检查样本的配对情况的原理是:他们首先从dbSNP数据库中选择了21067个位于外显子上的SNP用于预测样本配对。对于不用比对的fastq模式,他们在参考基因组中寻找了可以与参考基因组完全匹配的21bp长度的k-mer,位于这些k-mer上的SNP只剩下了11696个。然后用k-mer扫描fastq文件,计算每个SNP的VAF,再根据多个SNP的VAF计算样本间两两的相关性判断两个样本是否来源于一个人。 | |||||
|  | |||||
| # 流程与参数 | |||||
| - Required arguments | |||||
| `-l` 需要检测的fastq或者fastq.gz文件的表格,格式如下: | |||||
| ```bash | |||||
| FASTQ_FILE1 (tab) FASTQ_FILE2 (tab) SAMPLE_NAME (\n) | |||||
| Example: | |||||
| /data/LSJ_R1.fastq /data/LSJ_R2.fastq LSJ | |||||
| /data/LSH_R1.fastq /data/LSH_R2.fastq LSH | |||||
| ``` | |||||
| `-pt` 是一个包含SNP位点的二进制文件,这些位点可以用与样本的配对检查,在下载包中,路径为`SNP/SNP.pt` | |||||
| `-O` 输出文件夹 | |||||
| - Optional arguments | |||||
| `-N` 输出文件夹的前缀,default:“output” | |||||
| `-f` 当你的样本中有父母与孩子或者兄弟姐妹时,加上这个参数,使用更严格的VAF相关系数的阈值 | |||||
| `-nz` Use the mean of non-zero depths across the SNPs as reference depth, default: Use the mean depth across all the SNPs | |||||
| `-s` The read subsampling rate, default: 1.0 | |||||
| `-d` The target depth for read subsampling. NGSCheckMate calculates a subsampling rate based on this target depth. | |||||
| `-R` The length of the genomic region with read mapping (default: 3x10^9) used to compute subsampling rate. If your data is NOT human WGS and you use the -d option, it is highly recommended that specify this value. For instance, if your data is human RNA-seq, the genomic length with read mapping is ~3% of the human genome (1x10^8) | |||||
| 注意:如果你的fastq文件特别大,它的计算会特别慢,三个参数的使用可以通过subsampling的方法加快运算速度,文献中报道只要0.5X深度的数据就能有很好的预测效果,有两种选择: | |||||
| - 只使用 -s ,意思是fastq原始文件的百分之多少,如果你的fastq文件太大,运算速度很比较慢,可以使用其中一部分数据运算,不会影响运算结果,比如,30%就是`-s 0.3` | |||||
| - 需要通过使用-d 和-R | |||||
| `-L` The length of the flanking sequence of the SNPs, default: 21bp. It is not recommended that you change this value unless you create your own pattern file (.pt) with a different length. | |||||
| `-p` 线程数,default:1 | |||||
| # APP输入变量与输入文件 | |||||
| (1)准备样本文件 | |||||
| ```bash | |||||
| choppy samples NGScheckMates --output samples | |||||
| ``` | |||||
| samples文件中输入是 | |||||
| - fastq_dir | |||||
| fastq文件的地址,阿里云上的地址;如果需要使用多个项目的fastq文件,输入两个项目文件夹的上一级共同目录 | |||||
| - Input_file | |||||
| 一个txt文件,需要进行计算的文件的详细文件名,文件的地址按照要求修改 | |||||
| ```bash | |||||
| #read1 #read2 #sample_name | |||||
| /cromwell_inputs/*/directory_name/read1.fastq.gz /cromwell_inputs/*/directory_name/read2.fastq.gz sample_name | |||||
| ``` | |||||
| # APP输出结果 | |||||
| # 结果展示与解读 | |||||
+ 5
- 0
defaults
파일 보기
| { | |||||
| "docker": "registry.cn-shanghai.aliyuncs.com/pgx-docker-registry/ngscheckmate:v1.0.0", | |||||
| "disk_size": "100", | |||||
| "cluster_config": "OnDemand bcs.a2.3xlarge img-ubuntu-vpc" | |||||
| } |
+ 7
- 0
inputs
파일 보기
| { | |||||
| "{{ project_name }}.docker": "{{ docker }}", | |||||
| "{{ project_name }}.input_file": "{{ input_file }}", | |||||
| "{{ project_name }}.fastq_dir": "{{ fastq_dir }}", | |||||
| "{{ project_name }}.disk_size": "{{ disk_size }}", | |||||
| "{{ project_name }}.cluster_config": "{{ cluster_config }}" | |||||
| } |
BIN
picture/NGSMateCheck.png
파일 보기
BIN
tasks/.DS_Store
파일 보기
+ 29
- 0
tasks/NGScheckMates.wdl
파일 보기
| task NGScheckMates { | |||||
| File fastq_dir | |||||
| File input_file | |||||
| String docker | |||||
| String cluster_config | |||||
| String disk_size | |||||
| command <<< | |||||
| set -o pipefail | |||||
| set -e | |||||
| nt=$(nproc) | |||||
| export NCM_HOME=/opt/NGSCheckMate | |||||
| python /opt/NGSCheckMate/ncm_fastq.py -l ${input_file} -pt /opt/NGSCheckMate/SNP/SNP.pt -O '.' -p $nt -f -s 0.3 | |||||
| >>> | |||||
| runtime { | |||||
| docker:docker | |||||
| cluster:cluster_config | |||||
| systemDisk:"cloud_ssd 40" | |||||
| dataDisk:"cloud_ssd " + disk_size + " /cromwell_root/" | |||||
| } | |||||
| output { | |||||
| File all_txt="output_all.txt" | |||||
| File ncm="wd.txt" | |||||
| File cor_txt="output_corr_matrix.txt" | |||||
| File matched_txt="output_matched.txt" | |||||
| File r_script="r_script.r" | |||||
| } | |||||
| } |
+ 18
- 0
workflow.wdl
파일 보기
| import "./tasks/NGScheckMates.wdl" as NGScheckMates | |||||
| workflow {{ project_name }} { | |||||
| File fastq_dir | |||||
| File input_file | |||||
| String docker | |||||
| String cluster_config | |||||
| String disk_size | |||||
| call NGScheckMates.NGScheckMates as NGScheckMates { | |||||
| input: | |||||
| fastq_dir=fastq_dir, | |||||
| input_file=input_file, | |||||
| docker=docker, | |||||
| disk_size=disk_size, | |||||
| cluster_config=cluster_config | |||||
| } | |||||
| } |
Loading…